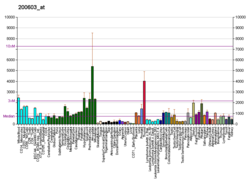
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I-alpha regulatory subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKAR1A gene.
Function
cAMP is a signaling molecule important for a variety of cellular functions. cAMP exerts its effects by activating the cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA), which transduces the signal through phosphorylation of different target proteins. The inactive holoenzyme of PKA is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. Four different regulatory subunits and three catalytic subunits of PKA have been identified in humans. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the regulatory subunits. This protein was found to be a tissue-specific extinguisher that downregulates the expression of seven liver genes in hepatoma x fibroblast hybrids Three alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been observed.
Clinical significance
Functional null mutations in this gene cause Carney complex (CNC), an autosomal dominant multiple neoplasia syndrome. This gene can fuse to the RET protooncogene by gene rearrangement and form the thyroid tumor-specific chimeric oncogene known as PTC2.
Mutation of PRKAR1A leads to the Carney complex, associating multiple endocrine tumors.
Interactions
PRKAR1A has been shown to interact with:
See also
References
- ^ GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000108946 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020612 – Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Scambler P, Oyen O, Wainwright B, Farrall M, Law HY, Estivill X, Sandberg M, Williamson R, Jahnsen T (December 1987). "Exclusion of catalytic and regulatory subunits of cAMP-dependent protein kinase as candidate genes for the defect causing cystic fibrosis". Am J Hum Genet. 41 (5): 925–32. PMC 1684338. PMID 3479018.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PRKAR1A protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type I, alpha (tissue specific extinguisher 1)".
- Huang LJ, Durick K, Weiner JA, Chun J, Taylor SS (October 1997). "D-AKAP2, a novel protein kinase A anchoring protein with a putative RGS domain". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (21): 11184–9. Bibcode:1997PNAS...9411184J. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.21.11184. PMC 23409. PMID 9326583.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (October 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- ^ Carlson CR, Ruppelt A, Taskén K (March 2003). "A kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) interaction and dimerization of the RIalpha and RIbeta regulatory subunits of protein kinase a in vivo by the yeast two hybrid system". J. Mol. Biol. 327 (3): 609–18. doi:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00093-7. PMID 12634056.
- Herberg FW, Maleszka A, Eide T, Vossebein L, Tasken K (April 2000). "Analysis of A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP) interaction with protein kinase A (PKA) regulatory subunits: PKA isoform specificity in AKAP binding". J. Mol. Biol. 298 (2): 329–39. doi:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3662. PMID 10764601.
- Brown PR, Miki K, Harper DB, Eddy EM (June 2003). "A-kinase anchoring protein 4 binding proteins in the fibrous sheath of the sperm flagellum". Biol. Reprod. 68 (6): 2241–8. doi:10.1095/biolreprod.102.013466. PMID 12606363.
- Miki K, Eddy EM (December 1998). "Identification of tethering domains for protein kinase A type Ialpha regulatory subunits on sperm fibrous sheath protein FSC1". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (51): 34384–90. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.51.34384. PMID 9852104.
- ^ Li H, Adamik R, Pacheco-Rodriguez G, Moss J, Vaughan M (February 2003). "Protein kinase A-anchoring (AKAP) domains in brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein 2 (BIG2)". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100 (4): 1627–32. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.1627L. doi:10.1073/pnas.0337678100. PMC 149883. PMID 12571360.
- Tortora G, Damiano V, Bianco C, Baldassarre G, Bianco AR, Lanfrancone L, Pelicci PG, Ciardiello F (February 1997). "The RIalpha subunit of protein kinase A (PKA) binds to Grb2 and allows PKA interaction with the activated EGF-receptor". Oncogene. 14 (8): 923–8. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1200906. PMID 9050991. S2CID 10640461.
- Küssel-Andermann P, El-Amraoui A, Safieddine S, Hardelin JP, Nouaille S, Camonis J, Petit C (September 2000). "Unconventional myosin VIIA is a novel A-kinase-anchoring protein". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (38): 29654–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M004393200. PMID 10889203.
- Taskén K, Skålhegg BS, Solberg R, Andersson KB, Taylor SS, Lea T, Blomhoff HK, Jahnsen T, Hansson V (October 1993). "Novel isozymes of cAMP-dependent protein kinase exist in human cells due to formation of RI alpha-RI beta heterodimeric complexes". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (28): 21276–83. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)36921-2. PMID 8407966.
- Ewing RM, Chu P, Elisma F, Li H, Taylor P, Climie S, McBroom-Cerajewski L, Robinson MD, O'Connor L, Li M, Taylor R, Dharsee M, Ho Y, Heilbut A, Moore L, Zhang S, Ornatsky O, Bukhman YV, Ethier M, Sheng Y, Vasilescu J, Abu-Farha M, Lambert JP, Duewel HS, Stewart II, Kuehl B, Hogue K, Colwill K, Gladwish K, Muskat B, Kinach R, Adams SL, Moran MF, Morin GB, Topaloglou T, Figeys D (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein-protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. 3: 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931.
Further reading
- Stratakis CA (2002). "Mutations of the gene encoding the protein kinase A type I-alpha regulatory subunit (PRKAR1A) in patients with the "complex of spotty skin pigmentation, myxomas, endocrine overactivity, and schwannomas" (Carney complex)". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 968 (1): 3–21. Bibcode:2002NYASA.968....3S. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04323.x. PMID 12119264. S2CID 26108486.
- Bourdeau I, Stratakis CA (2002). "Cyclic AMP-dependent signaling aberrations in macronodular adrenal disease". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 968 (1): 240–55. Bibcode:2002NYASA.968..240B. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04339.x. PMID 12119280. S2CID 22397904.
- Alto N, Carlisle Michel JJ, Dodge KL, Langeberg LK, Scott JD (2003). "Intracellular targeting of protein kinases and phosphatases". Diabetes. 51 (Suppl 3): S385–8. doi:10.2337/diabetes.51.2007.s385. PMID 12475780.
- Stergiopoulos SG, Stratakis CA (2003). "Human tumors associated with Carney complex and germline PRKAR1A mutations: a protein kinase A disease!". FEBS Lett. 546 (1): 59–64. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(03)00452-6. PMID 12829237. S2CID 37055425.
- Bossis I, Stratakis CA (2004). "Minireview: PRKAR1A: normal and abnormal functions". Endocrinology. 145 (12): 5452–8. doi:10.1210/en.2004-0900. PMID 15331577.
- Cho-Chung YS, Nesterova MV (2006). "Tumor reversion: protein kinase A isozyme switching". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1058: 76–86. doi:10.1196/annals.1359.014. PMID 16394127. S2CID 45471438.
- Lytras A, Tolis G (2006). "Growth hormone-secreting tumors: genetic aspects and data from animal models". Neuroendocrinology. 83 (3–4): 166–78. doi:10.1159/000095525. PMID 17047380. S2CID 45606794.
- Harrich D, McMillan N, Munoz L, Apolloni A, Meredith L (2007). "Will diverse Tat interactions lead to novel antiretroviral drug targets?". Current Drug Targets. 7 (12): 1595–606. doi:10.2174/138945006779025338. PMID 17168834.
- Boshart M, Weih F, Nichols M, Schütz G (1991). "The tissue-specific extinguisher locus TSE1 encodes a regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase" (PDF). Cell. 66 (5): 849–59. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90432-X. PMID 1832337. S2CID 8277752.
- Jones KW, Shapero MH, Chevrette M, Fournier RE (1991). "Subtractive hybridization cloning of a tissue-specific extinguisher: TSE1 encodes a regulatory subunit of protein kinase A". Cell. 66 (5): 861–72. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90433-Y. PMID 1889088. S2CID 24273073.
- Hofmann B, Nishanian P, Baldwin RL, Insixiengmay P, Nel A, Fahey JL (1991). "HIV inhibits the early steps of lymphocyte activation, including initiation of inositol phospholipid metabolism". J. Immunol. 145 (11): 3699–705. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.145.11.3699. PMID 1978848.
- Sandberg M, Skålhegg B, Jahnsen T (1990). "The two mRNA forms for the type I alpha regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase from human testis are due to the use of different polyadenylation site signals". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 167 (1): 323–30. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(90)91768-N. PMID 2310396.
- Lem J, Chin AC, Thayer MJ, Leach RJ, Fournier RE (1988). "Coordinate regulation of two genes encoding gluconeogenic enzymes by the trans-dominant locus Tse-1". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85 (19): 7302–6. Bibcode:1988PNAS...85.7302L. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.19.7302. PMC 282174. PMID 2902627.
- Sandberg M, Taskén K, Oyen O, Hansson V, Jahnsen T (1988). "Molecular cloning, cDNA structure and deduced amino acid sequence for a type I regulatory subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase from human testis". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 149 (3): 939–45. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(87)90499-2. PMID 3426618.
- Geahlen RL, Carmichael DF, Hashimoto E, Krebs EG (1982). "Phosphorylation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase subunits". Adv. Enzyme Regul. 20: 195–209. doi:10.1016/0065-2571(82)90016-4. PMID 6287816.
- Guild BC, Strominger JL (1984). "HLA-A2 antigen phosphorylation in vitro by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Sites of phosphorylation and segmentation in class i major histocompatibility complex gene structure". J. Biol. Chem. 259 (21): 13504–10. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)90722-2. PMID 6333425.
- Bongarzone I, Monzini N, Borrello MG, Carcano C, Ferraresi G, Arighi E, Mondellini P, Della Porta G, Pierotti MA (1993). "Molecular characterization of a thyroid tumor-specific transforming sequence formed by the fusion of ret tyrosine kinase and the regulatory subunit RI alpha of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase A". Mol. Cell. Biol. 13 (1): 358–66. doi:10.1128/MCB.13.1.358. PMC 358915. PMID 7678053.
- Hofmann B, Nishanian P, Nguyen T, Insixiengmay P, Fahey JL (1993). "Human immunodeficiency virus proteins induce the inhibitory cAMP/protein kinase A pathway in normal lymphocytes". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90 (14): 6676–80. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.6676H. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.14.6676. PMC 46995. PMID 7688126.
- Hofmann B, Nishanian P, Fan J, Nguyen T, Fahey JL (1994). "HIV Gag p17 protein impairs proliferation of normal lymphocytes in vitro". AIDS. 8 (7): 1016–7. doi:10.1097/00002030-199407000-00025. PMID 7946090.
External links
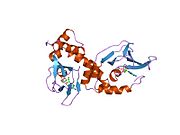
- PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Human cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I-alpha regulatory subunit (PRKAR1A)
| PDB gallery | |
|---|---|
|
| Intracellular signaling peptides and proteins | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAP | |||||||||||||||
| Calcium | |||||||||||||||
| G protein |
| ||||||||||||||
| Cyclin | |||||||||||||||
| Lipid | |||||||||||||||
| Other protein kinase |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other protein phosphatase |
| ||||||||||||||
| Apoptosis | |||||||||||||||
| GTP-binding protein regulators | |||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||
| see also deficiencies of intracellular signaling peptides and proteins | |||||||||||||||
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Categories: