| Transverse ligament of knee | |
|---|---|
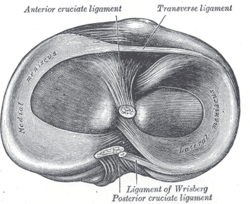 Head of right tibia seen from above, showing menisci and attachments of ligaments. (Transverse ligament labeled at upper right.) Head of right tibia seen from above, showing menisci and attachments of ligaments. (Transverse ligament labeled at upper right.) | |
| Details | |
| From | lateral meniscus |
| To | medial meniscus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | ligamentum transversum genus |
| TA98 | A03.6.08.006 |
| TA2 | 1889 |
| FMA | 76856 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The transverse or (anterior) meniscomeniscal ligament is a ligament in the knee joint that connects the anterior convex margin of the lateral meniscus to the anterior end of the medial meniscus.
It is divided into several strips in ten percent of subjects and its thickness varies considerably in different subjects.
Function
When the knee is being extended the ligament prevents the anterior horns of the menisci from moving forward, and the condylar surfaces of the femur and tibia from exerting pressure on the menisci. It has a restricting effect on anterior-posterior excursion of the anterior horn of the medial meniscus at lower degrees of knee flexion.
Prevalence of meniscomeniscal ligaments
The transverse ligament is reported in 58 per cent of subjects and is thus the most prevalent of four described meniscomeniscal ligaments. The other ligaments, all three of which are reported with a frequency of less than 4 per cent, are the posterior transverse ligament, described as a bundle of fibers connecting the posterior horns of the menisci; and the medial and lateral oblique ligaments, both of which originate on the anterior horn of their namesake meniscus, passes between the cruciate ligaments, and attaches to the posterior horn of the opposite meniscus. None of the oblique ligaments have a known function.
Formation
The formation of the transverse ligament has been investigated in human embryos aged 7–8 weeks (stages 18–23). At the early end of the range (stage 19), condensation of the mesenchymal interzone of the knee joint (i.e. the area of densely packed cells indicating the location of the future joint) was recognizable, and near the end of the range (stage 22) clearly visible cellular primordium of the ligament connected to both menisci was observed before all major intraarticular elements were finally evident (stage 23).
Notes
- Platzer (2004), p 208
- Behnke (2006), p 197
- Muhle et al. (1999)
- Sanders et al. (1999)
- Ratajczak (2001), pp 323-31
Additional Images
-
Anterior view of knee.
-
Knee and tibiofibular joint.Deep dissection. Anterior view.
-
Knee joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
References
- Behnke, Robert S. (2006). Kinetic Anatomy: The Essentials of Human Anatomy. Human Kinetics. ISBN 0-7360-5909-1.
- Muhle, Claus; Thompson, William O.; Sciulli, Robert; et al. (September 1999). "Transverse Ligament and Its Effect on Meniscal Motion: Correlation of Kinematic MR Imaging and Anatomic Sections". Investigative Radiology. 34 (9). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: 558–65. doi:10.1097/00004424-199909000-00002. PMID 10485070. Retrieved January 2, 2009.
- Platzer, Werner (2004). Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System (5th ed.). Thieme. ISBN 3-13-533305-1.
- Ratajczak, W. (November 2001). "Transverse ligament of the knee in human embryos aged 7 and 8 weeks". Folia Morphol (Warsz). 60 (4). Department of Anatomy, Karol Marcinkowski University School of Medical Sciences, Poznań, Poland.: 323–31. PMID 11770344. (PubMed abstract)
- Sanders TG, Linares RC, Lawhorn KW, Tirman PF, Houser C (1999). "Oblique Meniscomeniscal Ligament: Another Potential Pitfall for a Meniscal Tear-Anatomic Description and Appearance at MR Imaging in Three Cases". Radiology. 213 (1). RSNA: 213–216. doi:10.1148/radiology.213.1.r99oc20213. PMID 10540664. Retrieved January 2, 2009.
External links
- lljoints at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (antkneejointopenflexed)
- Ratajczak W, Jakubowicz M, Pytel A (2003). "Transverse ligament of the knee in humans". Folia Morphol. (Warsz). 62 (3): 293–5. PMID 14507071.
| Joints and ligaments of the human leg | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hip | |||||
| Knee |
| ||||
| Tibiofibular |
| ||||
| Foot | |||||