 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.355 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
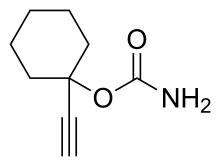
| Formula | C9H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 167.208 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Ethinamate (Valamin, Valmid) is a short-acting carbamate-derivative sedative-hypnotic medication used to treat insomnia. Regular use leads to drug tolerance, and it is usually not effective for more than 7 days. Prolonged use can lead to dependence.
Ethinamate has been replaced by other medicines (particularly benzodiazepines), and it is not available in the Netherlands, the United States or Canada.
It is a schedule IV substance in the United States.
Synthesis
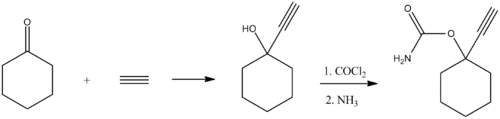
Ethinamate (1-ethynylcyclohexanone carbamate) is synthesized by combining acetylene with cyclohexanone to make 1-ethynylcyclohexanol, and then transforming this into a carbamate by the subsequent reaction with phosgene, and later with ammonia. Some lithium metal or similar is used to make the acetylene react with the cyclohexanone in the first step.
References
- Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-16.
- Lowry WT, Garriot JC (1979). "Ethinamate". Forensic Toxicology: Controlled Substances and Dangerous Drugs. Boston, MA: Springer US. p. 215. ISBN 978-1-4684-3444-6.
- US 2816910, Pfeiffer H, Junkman K, "Esters of carbamic acid and a method of making same", issued 17 December 1957, assigned to Schering AG
- DE 1021843, Emde H, Grimme W, "Verfahren zur Herstellung des Allophanats des 1-AEthinylcyclohexanols-(1)", issued 2 January 1958, assigned to Rheinpreussen AG
| GABAA receptor positive modulators | |
|---|---|
| Alcohols | |
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids |
|
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents | |
| Monoureides | |
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
| See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |
This sedative-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |