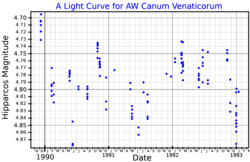
 A light curve for AW Canum Venaticorum, plotted from Hipparcos data | |
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Canes Venatici |
| Right ascension | 13 51 47.47504 |
| Declination | +34° 26′ 39.2474″ |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.76 (4.73 – 4.85) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | M3- IIIa |
| B−V color index | 1.611±0.006 |
| Variable type | Lb |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −44.21±0.25 km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −20.477 mas/yr Dec.: −31.626 mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 5.2734 ± 0.2529 mas |
| Distance | 620 ± 30 ly (190 ± 9 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −1.56 |
| Details | |
| Mass | 2.18±0.16 M☉ |
| Radius | 117.41+4.25 −4.57 R☉ |
| Luminosity | 2,387±213 L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.98±0.30 cgs |
| Temperature | 3,529±25 K |
| Metallicity | −0.09±0.11 dex |
| Age | 1.11±0.21 Gyr |
| Other designations | |
| AW CVn, BD+35° 2496, FK5 3102, HD 120933, HIP 67665, HR 5219, SAO 63793 | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
AW Canum Venaticorum is a variable star in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is visible to the naked eye with a nominal apparent visual magnitude of 4.76. The distance to this star, as measured from its annual parallax shift of 5.3 mas, is around 620 light years. It is moving closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −44 km/s.
The variability of the brightness of HR 5219 was announced by Joel Stebbins and Charles Morse Huffer in 1928, based on observations made at Washburn Observatory. It was given its variable star designation, AW Canum Venaticorum, in 1977.
At the age of 1.1 billion years, this is an evolved red giant star with a stellar classification of M3- IIIa. It is a slow irregular variable of type Lb, with a brightness that ranges between magnitudes 4.73 and 4.85. The star has 2.2 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 117 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 2,387 times the Sun's luminosity from its enlarged photosphere at an effective temperature of 3,529 K.
References
- "Hipparcos Tools Interactive Data Access". Hipparcos. ESA. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051.
- ^ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv:1108.4971, Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- ^ Samus', N. N; Kazarovets, E. V; Durlevich, O. V; Kireeva, N. N; Pastukhova, E. N (2017), "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1", Astronomy Reports, 61 (1): 80–88, Bibcode:2017ARep...61...80S, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, S2CID 125853869.
- ^ Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989), "The Perkins catalog of revised MK types for the cooler stars", Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 71: 245, Bibcode:1989ApJS...71..245K, doi:10.1086/191373, S2CID 123149047.
- ^ Baines, Ellyn K.; et al. (2018), "Fundamental Parameters of 87 Stars from the Navy Precision Optical Interferometer", The Astronomical Journal, 155 (1), 30, arXiv:1712.08109, Bibcode:2018AJ....155...30B, doi:10.3847/1538-3881/aa9d8b, S2CID 119427037.
- ^ Prugniel, P.; et al. (2011), "The atmospheric parameters and spectral interpolator for the MILES stars", Astronomy & Astrophysics, 531: A165, arXiv:1104.4952, Bibcode:2011A&A...531A.165P, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201116769, S2CID 54940439.
- "HD 120933". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 24 August 2018.
- Stebbins, Joel; Huffer, C. M. (1928). "The Constancy of the Light of Red Stars". Publications of the Washburn Observatory. 15: 137–174. Bibcode:1928PWasO..15..137S. Retrieved 5 December 2024.
- Kukarkin, B. V.; Kholopov, P. N.; Fedorovich, V. P.; Kireyeva, N. N.; Kukarkina, N. P.; Medvedeva, G. I.; Perova, N. B. (March 1977). "62nd Name-List of Variable Stars" (PDF). Information Bulletin on Variable Stars. 1248: 1–25. Bibcode:1977IBVS.1248....1K. Retrieved 8 December 2024.
| Constellation of Canes Venatici | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stars |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Galaxies |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||